Cloud computing is the delivery of computing resources as a service, meaning that the resources are owned and managed by the cloud provider rather than the end user. Those resources may include anything from browser-based software applications (such as Tik Tok or Netflix), third party data storage for photos and other digital media (such as iCloud or Dropbox), or third-party servers used to support the computing infrastructure of a business, research, or personal project. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), lists the following as the five essential characteristics of cloud computing:
Cloud & Digital Transformation
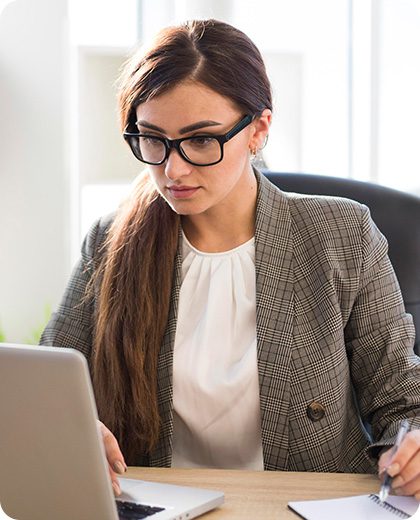

What is Cloud Computing?
On-demand self-service:
With this model, consumers can gain immediate access to cloud services upon signup. Organizations can also create mechanisms for allowing employees, customers, or partners to access internal cloud services on demand according to predetermined logics
Broad network access
: Users can access cloud services and resources through any device and in any networked location provided that they have permission.
Resource pooling
Cloud provider resources are shared by multiple tenants while keeping the data of individual clients hidden from other clients.
Rapid elasticity
cloud computing resources can be rapidly increased, decreased, or otherwise modified based on the cloud user’s changing needs.
Measured service
Usage of cloud resources is metered so that businesses and other cloud users need only pay for the resources they use in any given billing cycle.



Why is cloud & digital transformation important?
Digital transformation is when an organization takes advantage of new technologies to redesign and redefine relationships with their customers, employees, and partners. Digital transformation for business covers everything from modernizing applications and creating new business models to building new products and services for customers. Organizations choose digital transformation frameworks as a way to reimagine themselves staying competitive in their respective businesses and industries. Flexible technology to build, deploy, and manage applications more quickly in the cloud
- Flexible technology to build, deploy, and manage applications more quickly in the cloud
- Experimentation to embrace new ideas and gain new insights on customer and market demands
- Measurement of experimentation results with data analysis to guide decision-making
- Customer focus and data analysis to deliver greater value to customers
- Agility to scale and accelerate without hesitation to succeed in the digital age
Starting Your Journey Towards Digital Transformation and choose the Right Cloud Services for Your Business

Create a strategylogy
Digital transformation is like any other initiative: for it to be successful, you need a plan.

Pure Methodology
Lorem ipsum amet conectur adipisicing sed do eiusmod incididunt ut labore.

Startup Projects
Lorem ipsum amet conectur adipisicing sed do eiusmod incididunt ut labore.
-
What is microservices architecture?Microservices architecture (often shortened to microservices) refers to an architectural style for developing applications. Microservices allow a large application to be separated into smaller independent parts, with each part having its own realm of responsibility. To serve a single user request, a microservices-based application can call on many internal microservices to compose its response. Containers are a well-suited microservices architecture example, since they let you focus on developing the services without worrying about the dependencies. Modern cloud-native applications are usually built as microservices using containers
-
What is hybrid cloud?A hybrid cloud is one in which applications are running in a combination of different environments. Hybrid cloud approaches are widespread because many organizations have invested extensively in on-premises infrastructure over the past decades and, as a result, they infrequently rely solely on the public cloud. The most common example of hybrid cloud is combining a private computing environment, like an on-premises data center, and a public cloud computing environment, like Google Cloud
-
What is ETL?ETL stands for extract, transform, and load and is a traditionally accepted way for organizations to combine data from multiple systems into a single database, data store, data warehouse, or data lake. ETL can be used to store legacy data, or—as is more typical today—aggregate data to analyze and drive business decisions. Organizations have been using ETL for decades. But what’s new is that both the sources of data, as well as the target databases, are now moving to the cloud. Additionally, we’re seeing the emergence of streaming ETL pipelines, which are now unified alongside batch pipelines—that is, pipelines handling continuous streams of data in real time versus data handled in aggregate batches. Some enterprises run continuous streaming processes with batch backfill or reprocessing pipelines woven into the mix.
-
What is a data warehouse?Data-driven companies require robust solutions for managing and analyzing large quantities of data across their organizations. These systems must be scalable, reliable, and secure enough for regulated industries, as well as flexible enough to support a wide variety of data types and use cases. The requirements go way beyond the capabilities of any traditional database. That’s where the data warehouse comes in. A data warehouse is an enterprise system used for the analysis and reporting of structured and semi-structured data from multiple sources, such as point-of-sale transactions, marketing automation, customer relationship management, and more. A data warehouse is suited for ad hoc analysis as well custom reporting and can store both current and historical data in one place. It is designed to give a long-range view of data over time, making it a primary component of business intelligence.

